C++¶
约 1621 个字 153 行代码 预计阅读时间 8 分钟
Objects = Attributes + Services
C 语言:面向过程
C++:面向对象
语法细节 ¶
#include <>是系统目录;""在当前目录寻找
#include<iostream> #include<iostream.h>
::resolver
<ClassName>::<function name>
fields 成员变量
成员变量有类的作用范围
parameters 函数参数
local variable 本地变量
函数的作用变量
nullptr¶
c++ 不会把 void * 隐式转换成其他指针类型。
void f(int *);
void f(int);
define NULL = 0;
f(NULL);//报错
输入输出流 ¶
流读掉了就没有了,和 C 中随意读写不同
- extractors >>
- inserters <<
composition 组合 ¶
对象套对象
ways of inclusion
- fully
- by reference 指针
encapsulation 封装 ¶
把数据和操作数据的函数更加明确的方式绑定在一起,给予必要的访问控制,防止外部的随意调用
基本思想 ¶
- everything is an object
- a program is a bunch of objects 对象之间发送信息
- each object has its own memory made up of other objects
- every object has a type
- all objects of a particular type can receive the same message
:: - scope resolution operator 解析作用域
Inheritance 继承 ¶
拒绝 code duplication
刻画出派生类对象是基类对象的is-a-relationship形成hierachy of classes >,提高代码重用性。
allows sharing of design for
- member data
- member function
- interfaces
需要对原先的类进行扩充,形成 superset
- base class devire
- super class & sub class
- parent class & child class
class A{
private:
public:
};
class B:public A{
};
- 子类与父类出现同名函数,会自动隐藏掉父类函数
upcasting 向上适应 ¶
子类的对象可以当作父类看待
cast 是造型而不是类型转换
Polymorphism 多态 ¶
- upcast
- dynamic binding: call the funciton of the object
virtual内存开头都有一个隐藏的VPtr指针,指向VTable- 访问 Vtable 里面获得成员函数
Virtual Function¶
子类和父类的同名函数有联系
void render(Shape* p){
p->render();
//calls correct render function for givenShape!
}
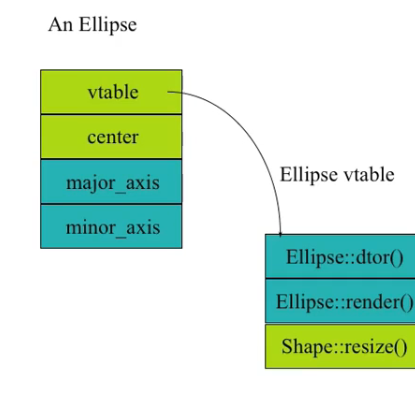
复制只是成员变量的复制
Virtual destructor¶
destructor 都是动态绑定的
override¶
只有指针和引用才构成 upcast 关系,直接返回子类对象是不构成的。
Overloading 重载 ¶
.h当中
default argument
编译时候进行
Stash(int size, int init = 0);
Stash(int size, int init = 0, int j);//illegal
类 ¶
object 这只杯子
class 杯子
class vs. struct
class default as private
声明和定义 ¶
声明 declaration ¶
把名字引入或者重新引入到程序当中
.h: 防止重复引用,要加入标准头文件结构
调用函数,和定义的时候都需要 include 这个头文件
extern global a;
// Type Alias
using arraylist = struct arraylist_ *;
//嵌套类,但是使用的时候需要写resolver
定义defination.cpp ¶
也是一种声明,引入的名字对应的实体可以被使用
类是图纸,对象是根据图纸创建的实例
函数是属于类的
Class Name {
private:
int i;
public:
Name();
~Name();
};//类后边要加一个分号
this hidden parameter, 指向该对象的指针
access - specifier¶
- public
- private
是对类来说的,而不是对对象来说的
自己指类的成员函数
权限限制仅在编译时刻
- protected
只有自己和子类可以访问
- friend
运算符的重载
可以声明自己是别人的朋友,授权别人访问自己的私有属性
constructor 构造函数 ¶
建立一种保证,要不是赋给的初值,要不然是改变后的值,不会是随机值
- 与类的名字相同
- 没有返回类型
- 不能放在
private里面
default constructor :没有参数的构造函数 ¶
Class Name {
private:
int i;
public:
Name();
~Name();
};//类后边要加一个分号
Name A[2]={A(1)} //会报错no matching funtion for call to A::A()
initializer list 初始化列表 ¶
早于构造函数执行
所有成员属性的赋值放在 initializer list 当中,对子类的初始化也放在 initializer list 当中
A():p(0){······}
Student::Student(string s):name(s){} // 初始化
Student::Student(string s) {name = s;} // 先初始化再赋值
如果成员有 const,也必须用 initializer list 进行初始化
只能初始化非静态成员,不能初始化 static
- c++ 初始化的时候,圆括号和等号是等价的
Virtual Constructor¶
拷贝构造 ¶
- 没有自己写的话,编译器会拷贝每一个对应的成员变量。不是 bit 对 bit 的拷贝,而是 member 对 member 的拷贝。
Person( const Person& w );
Person::Person( const Person& w ){
name = new char[::strlen(w.name) + 1];
::strcpy(name, w.name )//表示是外部的函数
}
- c++ 中字符串使用 string,可以用库中的拷贝构造
- 如果把拷贝构造函数私有,那么这个类的对象不可以作为函数的参数了
destructor 析构函数 ¶
Stroage allocation
相当于动态申请内存
new¶
先分配空间,再进行初始化
struct Foo{Foo(int x){printf("%d\n",x)}};
int main(){
Foo *p = new Foo(5);
Foo *pp = new Foo[](1,2,)
}
delete¶
先调用析构函数,再收回空间
delte的形式和new保持一致,要有括号都有括号
int * psome = new int [10];
delete [] psome;//析构函数调用次数不同,倒着顺序析构
delete psome;
inline function¶
调用函数开销比较大
.h:告诉编译器这是一个 inline 函数
不需要有.cpp
- 空间换时间,和宏类似,不过宏不可以类型检查
- 声明类的时候给出函数体,那么默认为内联函数
- 不是所有函数都需要并且适合内联。局部性和代码量会变差
- 可以进行类型检查、作用域、访问控制和括号,比宏更优
函数重载 ¶
先有默认参数,才有函数重载
实现方法:重载解析
先列出所有可能的函数,如果有一个函数优于其他所有的函数,那么就使用这个函数。如果没有,就报编译错误。
所以两个只有返回值类型不同的函数不是合法重载
const¶
编译器编译的时候,需要知道本地变量的大小
所以下面代码在报错
int x;
cin >> x;
const int size = x;
double classAverage[size]; //error!
char * const q = "abc"; // q是const
//*q = c; //ok
q++; //ERROR
const char *p = "ABCD";
// (*p) is a const char
*p = 'b'; //ERROR
Person p1("Fred",200);
const Person* p = &p1;
Person const* p = &p1;
Person *const p = &p1;
常量、全局变量放在代码段里面
函数 变量 放在堆栈
new 放在堆当中
以const身份传地址,比较安全
const 不能被修改
在函数后边加上 const 不会修改任何。在声明和定义的时候都要说明
函数后加 const 表明this为const
static¶
- 存储 static storage
- visibility of a name
static class
vptr:
第一次进入函数的时候进行初始化
全局变量的构造在第一个函数之前(main)
没有跨文件的初始化方案:所以将全局变量放在一个地方去
静态成员 ¶
静态成员变量需要在类外进行声明
class A{
public:
A():{i = 0}
~A():{}
private:
static int i;
}
int A::i;//不能再加static了
- 只能在定义的地方进行初始化,而不可以使用 initializer list
静态成员函数 ¶
没有创建任何一个对象实例之前,就可以访问这个函数
静态函数只可以访问静态成员变量
不可以调用 this
public:
static void say{}
A::say
reference - alias for an variable¶
实际是一个 const 指针
- no reference to reference
- no pointer to reference(reference to pointer is ok)
- no arrays for reference
char c;
char* p = &c;
char& r = c;//与别名类似
定义时候必须初始化
int* f(int *x){
(*x)++;
return x; // Safe,x is outside of this scope
}
int& g(int &x){
x++;
return x;
}
int x;
int& h(){
int q;
return x;// Safe, x lives outside of scope
}
int main(){
int a = 0;
f(&a);
g(a);
h() = 16;//reference 可以作为左值 也可以改变x的值
}
引用目标必须有地址,不能返回本地变量作为引用,而是应该返回全局变量作为 reference
函数范围一个引用的时候,直接返回一个变量
函数返回值为引用,则这个引用可以作为左值
double& subscript(const int i){
return array[i];
}
如果想传一个对象进入一个函数,使用 const reference
Template 模板 ¶
XY 有一个基类
类型作为参数
函数模板 Function template
类模板 Class template
template < class T > //declaration
void swap( T& x, T& y ) {
T temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
//can be explicit
template < class T >
void foo( void ){}
foo<int>();
foo<float>();
template< class Key, class Value >
template< class T, int bounds = 100 >
FixedVector<int,50>
告诉编译器如何做一个函数
参数类型、返回类型
不可以进行类型转换
模板和继承 ¶
种的时候,每一个类都是父类的子类
template<class A>
class Derived : public List<A>{
}
STL¶
运算符的重载 ¶


给运算符一个运算规则
const String String::operator + (const String& that)
class Integer {
public:
Integer( int n = 0) : i(n){}
const Integer operator+(const Integer& n) const{
return Integer(i + n.i);
}
private:
int i;
}
用左边成员receiver
z = x+y; z=x+3;是可以的
z = 3+y是不行的。
重载也可以写成全局函数
异常 ¶
exception
if(index < 0 || index >= size){
throw VectorIndexError(index);
}
try{
func();
}catch(VectorIndexError& e){
e.diagnostic();
}
//异常的传播机制
try{
} catch(...){
}
//函数声明,限制abc
void abc(int a) : throw(MathErr){
}