01 | 神经网络 ¶
约 1003 个字 预计阅读时间 4 分钟
训练(Training) 打个比方,你现在想要训练一个能区分苹果还是橘子的模型,你需要搜索一些苹果和橘子的图片,这些图片放在一起称为训练数据集(training dataset),训练数据集是有标签的,苹果图片的标签就是苹果,橘子亦然。一个初始神经网络通过不断的优化自身参数,来让自己变得准确,可能开始10张苹果的照片,只有5张被网络认为是苹果,另外5张认错了,这个时候通过优化参数,让另外5张错的也变成对的。这整个过程就称之为训练(Traning)。
推理(Inference) 你训练好了一个模型,在训练数据集中表现良好,但是我们的期望是它可以对以前没看过的图片进行识别。你重新拍一张图片扔进网络让网络做判断,这种图片就叫做现场数据(live data),如果现场数据的区分准确率非常高,那么证明你的网络训练的是非常好的。我们把训练好的模型拿出来遛一遛的过程,称为推理(Inference)。
部署(deployment) 想要把一个训练好的神经网络模型应用起来,需要把它放在某个硬件平台上并保证其能运行,这个过程称之为部署(deployment)。
activation function¶
神经网络有了激活函数,才能进行非线性变换
sigmoid¶
s 形函数
优良性质
Tanh¶
takes a real-valued number and “squashes” it into range between -1 and 1
- Like sigmoid, tanh neurons saturate
- Unlike sigmoid, the output is zero-centered o It is therefore preferred than sigmoid
- Tanh is a scaled sigmoid: \(tanh(x) = 2 * \sigma(2x) − 1\)
ReLU¶
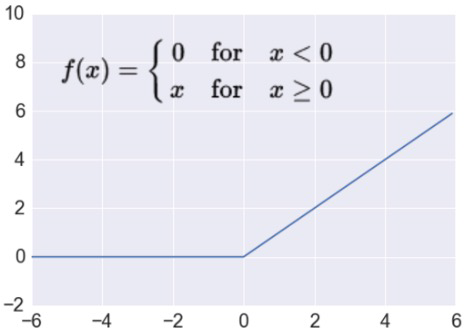 ReLU is fast to compute
ReLU is fast to compute
- Compared to sigmoid, tanh
- Simply threshold a matrix at zero
- Accelerates the convergence of gradient descent
- Due
- linear, non-saturating form
- Prevents the gradient vanishing problem
导数非 0 的区域更大
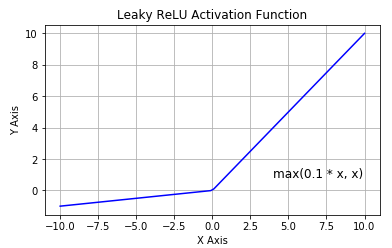
Leaky ReLU¶
超参数 | hyper parameters ¶
The most common hyper-parameters include: § Number of layers, and number of neurons per layer § Initial learning rate § Learning rate decay schedule (e.g., decay constant) § Optimizer type • Other hyper-parameters may include: § Regularization parameters (ℓ" penalty, dropout rate) § Batch size § Activation functions § Loss function
Grid search § Check all values in a range with a step value • Random search § Randomly sample values for the parameter § Often preferred to grid search • Bayesian hyper-parameter optimization § Is an active area of research
Learning Rate¶
Learning rate scheduling is applied to change the values of the learning rate during the training § Annealing is reducing the learning rate over time (a.k.a. learning rate decay) o Approach 1: reduce the learning rate by some factor every few epochs – Typical values: reduce the learning rate by a half every 5 epochs, or divide by 10 every 20 epochs o Approach 2: exponential or cosine decay gradually reduce the learning rate over time o Approach 3: reduce the learning rate by a constant (e.g., by half) whenever the validation loss stops improving
§ Warmup is gradually increasing the learning rate initially, and afterward let it cool down until the end of the training
regularization¶
正则化约束参数的大小
如何验证正则化的大小
dropout¶
Randomly drop units (along with their connections) during training § Each unit is retained with a fixed dropout rate p, independent of other units § The hyper-parameter p needs to be chosen (tuned) o Often, between 20% and 50% of the units are dropped
Early-stopping¶
Batch normalization layers
多层感知机 ¶
- 多层感知机在输出层和输入层之间增加一个或多个全连接隐藏层,并通过激活函数转换隐藏层的输出。
- 常用的激活函数包括 ReLU 函数、sigmoid 函数和 tanh 函数。
共享参数通常可以节省内存,并在以下方面具有特定的好处:
对于图像识别中的 CNN,共享参数使网络能够在图像中的任何地方而不是仅在某个区域中查找给定的功能。 对于RNN,它在序列的各个时间步之间共享参数,因此可以很好地推广到不同序列长度的示例。 对于自动编码器,编码器和解码器共享参数。 在具有线性激活的单层自动编码器中,共享权重会在权重矩阵的不同隐藏层之间强制正交。